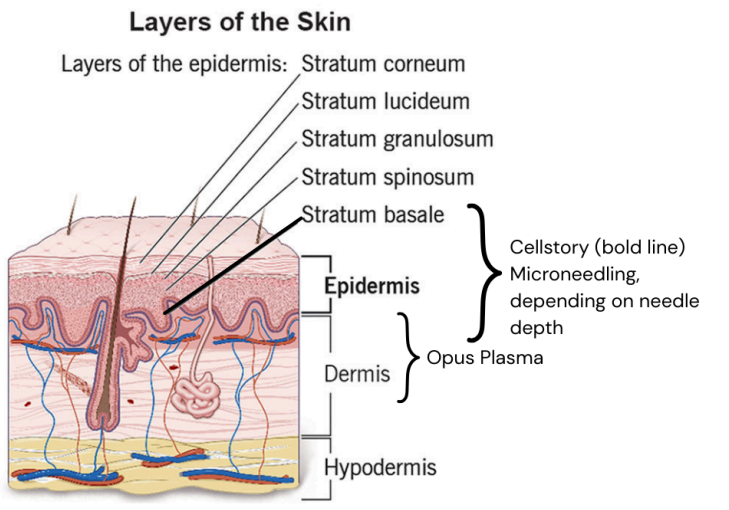
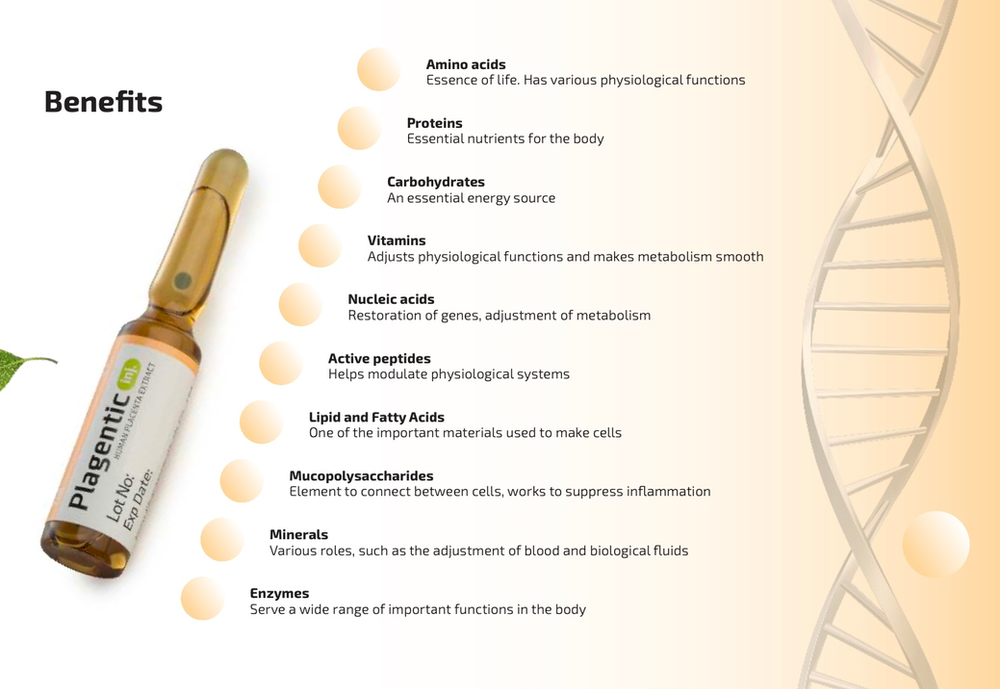
Introducing Cellstory™ Liquid Microneedling:A First in the Twin Ports
Red light therapy can safely treat a variety of conditions from aging to injuries to chronic pain. Conditions red light can be effective in treating include:
Stubborn fat
Red light therapy helps release fat stored in cells around your body. It can be effective in getting rid of stubborn fat, and has been shown to be effective in as little as 4 weeks (even without making other diet or lifestyle changes).
Fat cells may be hard and stubborn, but they’re no match for the infusion of 635nm red light and 880nm near infrared light in our red-light therapy sessions!
The energy from the near infrared light weakens the cell lining and opens pores in the fat cells. This allows the fat to be released. After exposure to these specific wavelengths, seventy to ninety-nine percent of the fat may be released from each cell, to be processed by the lymphatic system and stored in other tissues (like muscle) or metabolized for energy. While the fat is purged, the cell itself remains healthy and viable. This means it will refill with fat if you take in more calories than you need for fuel.
The fat cells remain energized for approximately 48 hours after a red-light therapy session. During this time, they shrink, and the skin will tighten due to the increase in collagen production stimulated by the red-light therapy.
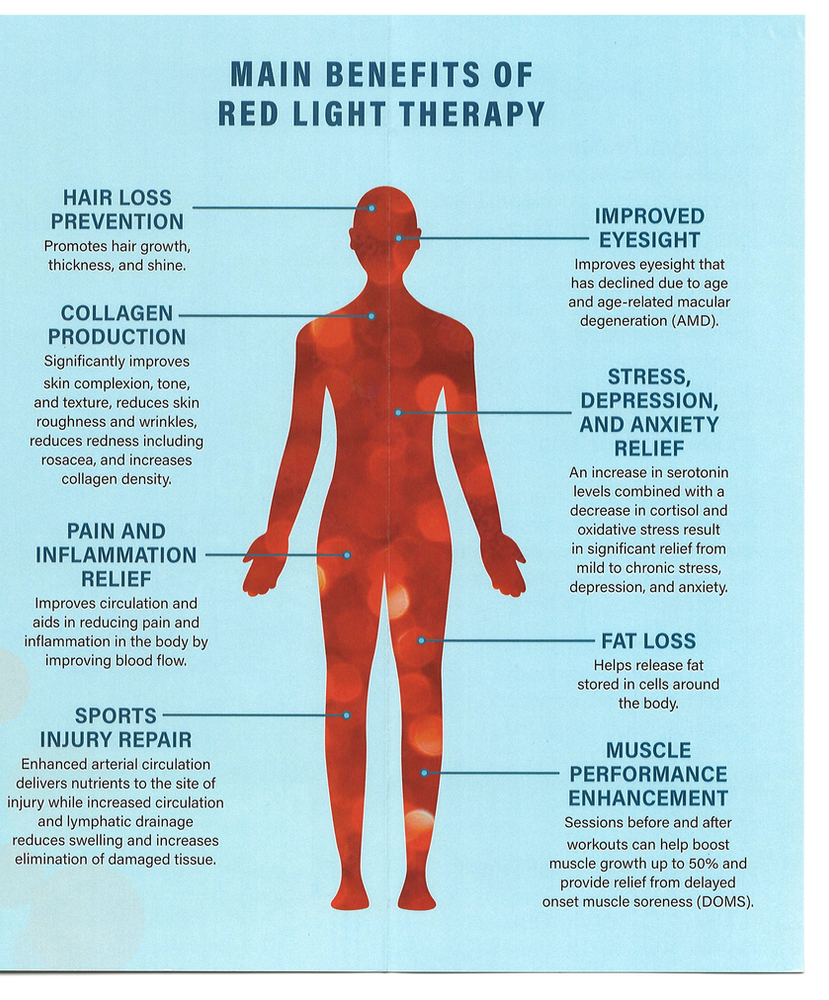
Fat loss benefits of red-light therapy
-
Red-light therapy has been shown to enhance the effects of physical exercise, resulting in greater loss of fat mass while increasing metabolic activity
-
Red-light therapy is a non-invasive treatment to help reduce circumference in specifically treated areas like the waist, hips, and thighs.
-
Red-light therapy can be effective at increasing fat loss, even without changes to diet or exercise habits . (Though as we noted above, it’s even more effective when coupled with diet/lifestyle changes!)
-
Research suggests that red-light therapy may be an effective, stand-alone treatment for improving the appearance of cellulite .
-
Red-light therapy helps reduce fat throughout the body , not just in specifically treated areas.
-
Unlike other fat loss methods, systems, and treatments, red-light therapy may work for everyone .
-
Inflammation
Research has shown it to be effective in reducing pain and inflammation in the body by improving blood flow, reducing markers of oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory proteins, and may even have wide-reaching, systemic anti-inflammatory benefits.
Inflammation is a normal biological response triggered by an injury or assault to the body. When an injury or infection is detected, the body supplies the inflamed area with more blood flow and oxygen so the injured cells can heal and regenerate. As the site heals, the inflammation recedes.
There are two types of inflammation, acute and chronic.
Acute Inflammation occurs when the body is injured or there is an infection. Signs of acute inflammation include the well-known signs of swelling, redness, tenderness, and pain.
Chronic inflammation is typically a low-grade internal inflammation that lasts for months, even years. While acute inflammation is essential to helping us heal, chronic inflammation can be much more problematic.
Vision issues
There is promising research that suggests red light therapy may help improve the health of your eyes and improve conditions such as age-related macular degeneration.
Red light therapy has been shown to be a safe, effective, non-invasive treatment option to help improve and maintain eye health.
Near infrared light has been shown to be enormously beneficial in the treatment of vision issues such as macular degeneration, retinal stress, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal degeneration. Red light therapy has shown promise in reducing retinal inflammation, improving retinal healing, delaying aging retinal functions, and inhibiting the degeneration of injured optic nerve and retina.
How can red light therapy help improve eye health?
Research supporting the benefits of red-light therapy for eye health continues to grow. Currently, red light therapy has been shown to :
-
Penetrate diseased retina to promote mitochondrial energy production and function.
-
Elevate cytoprotective factors for up to a month.
-
Prevent the death of photoreceptors by up to 70%.
-
Inhibit the cellular degeneration of retinal ganglion cells.
-
Reduce oxidative stress.